The technologies are changing from time to time. New systems are developed. So Engineering
systems nowadays are becoming more and more complex due to application of automation,
miniaturization, embedded technology, presence of software-hardware interfaces and its
interdisciplinary nature. Concern for environment, cost of failures and associated down times,
safety of operation, effectiveness of maintenance are also becoming important considerations.
Failure of the engineering systems in the past has resulted in the damage to property and
environment. So the concepts of reliability engineering helps us to find our ways to improve the
performance and safety. Reliability is one of the most important performance characteristics of
engineering systems. Reliability engineering is an interdisciplinary branch that focuses on the
systematic study of failures of engineering components and systems.
BATH TUB CURVE
Bathtub curve represents the probability of failure or hazard rate behavior of the system and
equipment. In the bathtub hazard curve, the failure rate or probability of failure within the total
life cycle time of equipment is clearly represented by three stages of hazards . The three stages of
hazards are low hazard zone, constant and moderate hazard zone and high hazard rate zone. The
first part that is Stage –I is a decreasing failure rate (low hazard zone) known as early failures. It
is also known as burn-in zone, break-in zone, or infant mortality region. Region for occurrence
of such failure may be due to the use of substandard material, poor workmanship, poor quality
control, human error, faulty design and manufacturing defect. The second part that is stage –II is
a constant failure rate (moderate hazard zone), known as random failure. This stage is widely
known as useful life period. The reason for such failure is due to constant use and high random
stresses developed, not maintaining proper safety factor, operational and human error or
otherwise natural failure. The third part that is stage-III is an increasing failure rate (high hazard
zone), known as wear-out failure. The reason for the failure is due to wear-out caused by
prolonged use and aging, excessive friction poor maintenance, corrosion and fatigue or creep
failure.
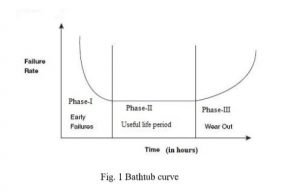
Therefore, in the bath tub curve, stage –I represent infant mortality failures, stage –II represents
the rate of random failures with constant failure during its “ useful life” and finally stage –III
represents the rate of wear –out failures as the product exceeds its design life time.
