Importance of Profibus
In an industrial automation system, communication between PLC, SCADA, HMI or any other automation devices is essential to pass information. Process field bus, Profibus is actually an industrial communication protocol used for real-time data exchange. Profibus, which can perform complex communication task is best suitable for fast and time-critical applications.
 Communication protocol
Communication protocol
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more devices to transmit data through a physical quantity. A protocol can cover semantics, syntax, and synchronization of analog and digital communications. It can also cover authentication, signaling and error detection. To transfer information, a single multi-drop cable is used to connect all devices with high speed, bi-directional and serial messaging. This one uses a bus topology. Which means, all the devices are connected to one central line.
 Profibus types
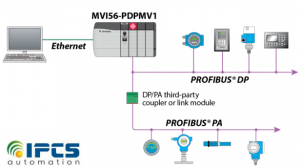
Profibus types
Mainly, Profibus have two types. Profibus PA and Profibus DP, where PA and DP indicate process automation and decentralize peripheral respectively. Profibus PA is designed with a motive to replace conventional systems such as 4-20mA and HART in process automation. Saving in cable, asset management, exchangeable without configuration changes are the major benefits of Profibus PA.
Considering the most used Profibus, Profibus DP can be called as the most used fieldbus worldwide in the production environment. This high-speed solution for Profibus is standardized under IEC 61158. Which means it is compatible with devices from different manufacturers. Profibus DP is designed specifically for communication between automation systems and decentralized equipment. In 90% of the applications, slave Profibus utilize the Profibus DP. The operator can select data transmission speed between 9.6kbps and 1.6mbps and is configured in the master. High data speed, low connections cost, plug, and play are the other advantages.
Profibus is a master-slave protocol to allow for multiple masters. There is no direct information exchange between the slaves. The master devices ask for data and the slave responds to it. This master-slave configuration is simpler to analyze than high-level networks such as TCP/IP.
