RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
falls under the sort of broad range of circuit breakers. As we know there are mass types of miniature circuit breakers like MCCB which works on diverse operational principles and has various safety scopes.
Function: Residual Current Circuit Breaker is virtually a device that senses current and disconnects any low voltage (unbalanced current) circuit whenever there is any fault that occurs.
Purpose: Residual Current Circuit Breaker essentially is installed to avert human from shocks or death caused by shocks. It prevents accidents by disconnecting the main circuit within a fraction of seconds.

How Residual Current Circuit Breaker Works?
It has very simple working based on Kirchhoff’s Current Law the incoming current in a circuit must be equal to the outgoing current from that circuit. This circuit breaker is made like that whenever a fault occurs the current balance of line and neutral did not match (imbalance occurs, as the fault current finds one more earth path of current).
Its circuit is made such that every instance it compares the value of incoming and outgoing circuit current. Whenever it is not equal, the residual current which is basically the difference between the two currents actuates the circuit to trip/switch off.
Working Principle of Residual Current Circuit Breaker:
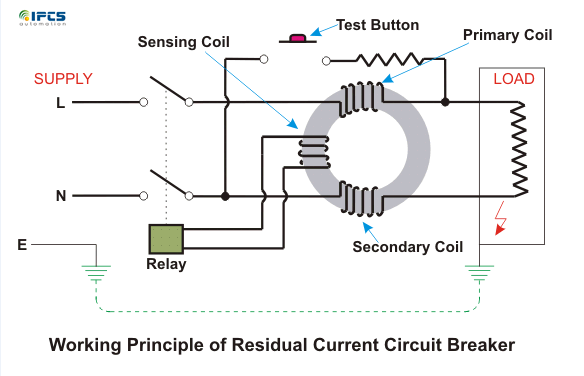
The basic operating principle lies in the Toroidal Transformer shown in the diagram that contained three coils. There are two coils say Primary (contained line current) and Secondary (contained neutral current) which produces equal and opposite fluxes if both currents are identical.
Whenever in the case there is a fault and both the currents changes, it creates out of balance flux, which in turn produces the differential current which flows through the third coil (sensing coil displayed in the figure) which is combined to relay.
The Toroidal transformer, sensing coil and relay along is known as RCD – Residual Current Device.
Test Circuit:
The test circuit is always included with the RCD which essentially combined between the line conductor on the load side and the supply neutral. It helps to test the circuit when it is on or off the alive supply. Whenever the test button is nudged current starts falling through the test circuit depending upon the resistance provided in this circuit. This current flowing through the RCD line side coil along with load current. But as this circuit bypasses the neutral side coil of RCD, there will be an unbalance between the line side and neutral side coil of the device and therefore, the RCCB trips to disconnect the supply just in normal condition. This is how the test circuit tests the accuracy of RCCB.
Types of RCCBs:
2 Pole RCCB:
It is used in single-phase supply cases. Mostly that involves only a live and neutral wire. It contains two ends. On these, the life and the neutral wires are connected. A Rotary switch is also worn. It is used to switch the RCCB back to ON or OFF positions. A test button helps to test the RCCB functionality.
4 Pole RCCB:
It is used in three-phase supply cases. It involves three phase wires and a neutral wire. It consists of two ends where the three phases and the neutral wire is connected. In construction and operation, it is like 2 Pole RCCB. In both these types of RCCBs, a Rotary switch is used. This helps in switching the RCCB back to ON or OFF positions. A test button is also provided to test the RCCB functionality.
Benefits Of RCCB:
- Provides protection against earth fault
- Provides protection against any leakage current
- Automatically disconnects the circuit when the rated sensitivity is outstripped
- Offers the possibility of dual termination both for cable and busbar connections
- Offers protection against voltage fluctuation.
- Guards against transient voltage levels.
