
6G Mobile Technology

The term 6G stands for the sixth generation of wireless technology. It is proposed to integrate advanced features in the existing 5G technology to fulfill objectives at individual and group levels. Some of the 6G services include holographic communications, Artificial intelligence, high precision manufacturing, and new technologies such as sub-THz or VLC (Visible Light Communications), and 3D coverage framework, terrestrial and aerial radio APs to provide cloud functionalities and so on.

At the time of writing as in June 2019, 5G has been installed and tested in major cities of USA by Sprint, Verizon, and T-Mobile whereas 6G wireless is undergoing research. Companies such as Samsung and SK Telecom have started research in the 6G wireless technology domain. Moreover, SK telecom has joined hands with Ericsson and Nokia for research in 6G technology. 6G uses cell-less architecture in which UE connects to the RAN and not to a single cell
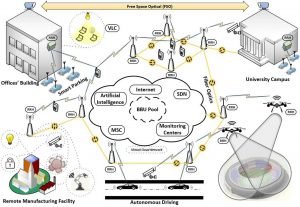
The following are the key technical features introduced in 6G wireless.
- New Spectrum: Due to the increase in traffic demand and scarcity of spectrum resources THz (Terahertz) and Visible light bands have been introduced for communication in the 6G mobile communication system.
- New channel coding has been introduced based on Turbo, LDPC, Polar, etc.
- Sparse theory (compressed sensing)
- Very large scale antenna processing for THz
- Advanced signal processing
- Flexible spectrum (Full (free) spectrum, Spectrum sharing)
- AI-based on wireless communication
- Space-Air-Ground-Sea integrated communication
- Wireless Tactile Network
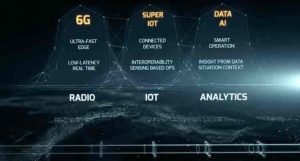
5G VS 6G
| Features | 5G | 6G |
| Frequency Bands | • Sub 6 GHz, • mm-wave for fixed access | • mm-wave for mobile access exploration of THz bands (above 140 GHz), • Non-RF bands (e.g. optical, VLC) etc.• Sub 6 GHz, |
| Data rate | 1 Gbps to 20 Gbps (Downlink Data Rate – 20 Gbps, Uplink Data Rate – 10 Gbps) | 1 Tbps |
| Latency (End to End Delay) | 5ms (Radio: 1msec) | < 1ms (Radio : 0.1msec) |
| Architecture | • Dense sub 6 GHz smaller BSs with umbrella macro BSs • Mm wave small cells of about 100 meters (for fixed access) • | Cell-free smart surfaces at high frequencies ( mm-wave tiny cells are used for fixed and mobile access) • Temporary hotspots served by drone-mounted BSs or tethered Balloons. • Trials of tiny THz cells (under progress)
|
| Application types | • eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) • URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications) • mMTC (Massive Machine Type Communications)
| • MBRLLC • Murllc • HCS • MPS |
| Device types
| • Smartphones • Sensors • Drones | • Sensors & DLT devices • CRAS • XR and BCI equipment • Smart implants |
| Spectral and energy efficiency gain | 10 x in bps/Hz/m2 | 1000 x in bps/Hz/m3 |
| Traffic Capacity | 10 Mbps/m2 | 1 to 10 Gbps/m2 |
| Reliability | 10-5 | 10-9 |
| Localization precision | 10 cm for 2D | 1 cm for 3D |
| User experience | 50 Mbps 2D everywhere | 10 Gbps 3D everywhere |
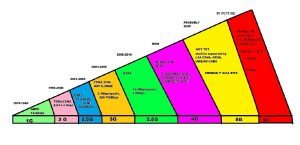
Evolution of Technology in Mobile
6G Increase the performance and maximize your data throughput and IOPS
- Its Protect your system and secure your data
- It can be Ease your service and build efforts and expand your data center configuration options
Iops = (Input/Output Operations per Second, pronounced eye-ops)
(With the answer typically converted to Megabytes per Sec)
6G speeds are fast approaching the importance of electronics in the modern world is hard to overstate, touching every aspect of life.
Telecommunications offers a striking example of the quickness of the electronics revolution. The move from 1G to 4G took a full decade. The footstep of new technologies is moving faster, meaning that the time to 5G and 6G will be much shorter, it may be a little as three years until 6G is a reality.
What are the driving forces behind this revolution? One important key factor is the proceed with the evolution of the integrated circuit (IC) toward higher speeds and lower power consumption, providing the ability to make products of all kinds smaller and more powerful. Today, ICs are the brains of a wide range of consumer products, from personal computers and smartphones to entertainment devices, automobiles, and home appliances.
The different core of industrial products such as industrial types of machinery and equipment, medical devices, renewable energy equipment, oil and gas exploration systems, digital homes, networking components, process control equipment, aircraft, and construction equipment. At the system level, designers are being asked to pack more and more capability into devices and electronic systems with ever-diminishing dimensions. The designers of today’s smartphones have to introduce new products that are lighter and thinner — and more frequently than before, on an annual basis. At the same time, the telecommunications equipment industry must continue to make faster and faster networking devices to accommodate the increasing traffic caused by these next-generation smart devices.
In such an environment, every design decision, from the choice of components to the location of ports and switches, infects every aspect of the product. Taken together, these trends create challenges for designers in several areas: Signal integrity (SI) and electromagnetic interference: Signals are closer together in chips, on printed circuit boards (PCBs), inside product enclosures and in cables. Therefore, it is more likely that electromagnetic fields from one signal could interfere with and distort an adjacent signal, resulting in a product defect.
Thermal performance: Higher current densities in chips, PCBs and cables can create hot spots, influencing signal timing and potentially leading to component failures. In some cases, a component can fail because the temperature overflows the limit of the materials. But even temperatures below the threshold can make failures due to electro migration. The Race to 6G — Faster Networks and Devices Promise a World of New Possibilities and realities.

Goal
The goal of 6G technology is to fulfill the vision of 5G technology and in addition to meet Wisdom connection, Deep connectivity, Holographic connectivity, and Ubiquitous connectivity. 5G accommodates different types of networks whereas 6G aggregates them dynamically.

