Skip to content
Night vision in security camera
IPCS Global November 18, 2019 Night vision in security camera:
CONTENTS: Introduction Types of Night Vision Working of Technical Night Vision Night Vision Devices Generations Applications Conclusion Reference
INTRODUCTION: Night vision technology, literally allows one to see in the dark. It is originally developed for military use . Humans have poor night vision compared to many other animals. With the proper night-vision equipment, we can see a person standing over 200 yards (183 m) away on a moonless, cloudy night. TYPES OF NIGHT VISION: It is broadly classified into two types Biological Night Vision Molecules in the rods of the eye undergo a change in shape as light. Molecules in the human rods is insensitive to the light. Technical Night Vision Image intensifier Thermal imaging
WORKING OF TECHNICAL NIGHT VISION:
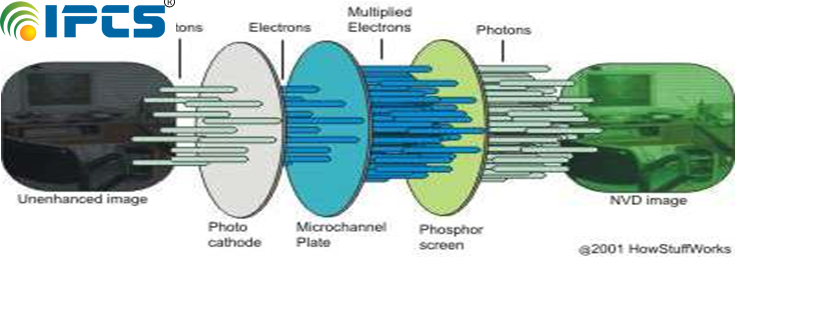
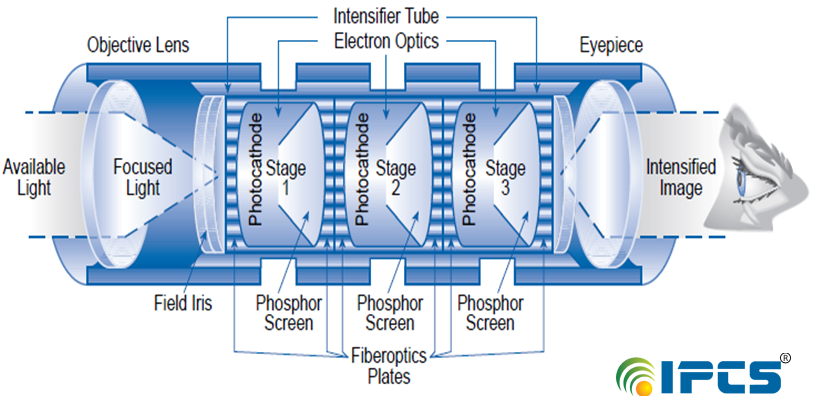
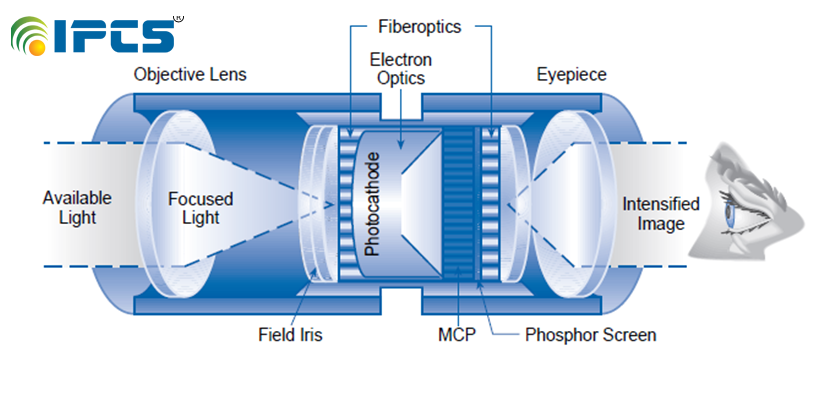
Technical Night vision can work in two very different ways Image Intensifier Night vision amplifies light to achieve better vision . A conventional lens, captures ambient light. The gathered light is sent to the image-intensifier tube. The light energy released electron from the cathode and These electrons enter micro channel plate and bounce off and generate more electron. Thousands of other electrons to be released in each channel. Original electrons collide with the channel,exciting atoms and causing other electrons. New electrons collide with other atoms, creating a chain. In image-intensifier tube, the electrons hit a screen. The energy of the electrons release photons and create green image on the screen. The green phosphor image is viewed through another lens.
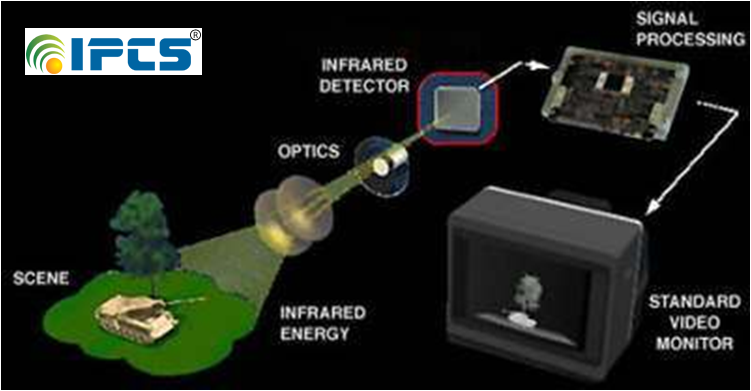
Thermal Imaging: All objects emit infrared energy as a function of their temper ature.A lens focuses the infrared light. The focused light is scanned and create temperature pattern. The pattern created is translated into electric impulses. The impulses are sent to a circuit board that translates the information into data for the display. The signal-processing unit sends the information to the is play, and appears as various colors. Thermal images are black and white in nature.
Night vision devices are basically divided into three categories SCOPES They are monocular normal handheld or mounted on a weapon GOGGLES They are binocular and worn on the head. CAMERAS Used for transmission or recording of images mostly if the location is fixed
GENERATIONS: Generation 0 The earliest (1950’s) night vision products were based on image conversion, rather than intensification Generation 1 Vacuum Tube Technology Full Moon Operation Amplification: 1,000 Operating Life: 2,000 Hours
Generation 2 First Micro channel Plate Application One-Quarter Moon Operation Amplification: 20,000 Operating Life: 2,500 Hours Generation3 Improved Micro channel Plate & Photocathode Starlight Operation Amplification: 40,000 Operating Life: 10,000 Hour
APPLICATIONS: Military Hunting Wildlife observation Security Hidden-object detection ADVANTAGES: No particular skill required Accidents cases reduction Compact system 3x range visual DISADVANTAGES: The only disadvantage is that the Initial cost too high.
Address
Hours
This may be a good place to introduce yourself and your site or include some credits.
Address
Hours
This may be a good place to introduce yourself and your site or include some credits.
Automation Training Our foundation-to-advanced automation course training covers end-to-end industrial workflows used in modern plants. Learners practice the full cycle from basic circuits to commissioning and maintenance with hands-on labs, project-based fault finding, SOP creation, and documentation exposure (URS, FDS, FAT/SAT).
PLC Training This PLC training builds controller fundamentals with ladder, FBD, and ST, including I/O wiring, PID tuning, diagnostics, and version control practices on live rigs.
SCADA Training Our SCADA course covers tag databases, HMI graphics, historian/trends, alarm rationalization, redundancy, user security, backups, and deployment aligned to plant standards.
Panel Designing This panel design course teaches standards-compliant MCC/PLC panel engineering, SLD/GA/wiring docs, device selection, heat-load, testing, and FAT.
BMS & Security BMS training focuses on HVAC/lighting/utilities automation; CCTV & security covers design, storage, networking, and analytics.
IIoT The Industrial IoT diploma spans sensors-to-dashboard pipelines: MQTT/OPC UA, gateways, historians, alerts/KPIs, and predictive maintenance basics.
Locations:
Mumbai (Vashi),
Pune (Chinchwad),
Maharashtra ,
Kolkata ,
West Bengal ,
Madhya Pradesh ,
Chhattisgarh ,
Jharkhand ,
Hyderabad (Ameerpet),
Bangalore (JP Nagar),
Mysore (Vijayanagar 2nd Stage),
Karnataka ,
Chennai (Anna Nagar West Extn),
Tambaram (West Tambaram),
Tamil Nadu ,
Tiruchirappalli (Chatram),
Erode ,
Madurai (K. Pudur),
Tirunelveli (Vasanth Nagar),
Coimbatore (Hope College),
Palakkad (Sultanpet),
Pathanamthitta (Chittoor),
Kottayam ,
Malappuram (Perinthalmanna),
Thrissur (Keerankulangara),
Kannur (Thana),
Kollam (Chinnakada),
Thiruvananthapuram (Thampanoor),
Kozhikode (Mavoor Rd Jn),
Kochi (Kaloor)