Human Machine Interface (HMI)
Human-machine interface, in its simplest terms, includes software or any device that allows you to interact with a machine. It can be as present and simple as the traditional single-touch display mounted on a machine or as technologically advanced as a multi-touch-enabled control panel or even connected new mobile technology such as smartphones and smartwatches.HMI, it is considered an interface that allows human beings to interact with a machine. Examples of HMI physical aspects could be a machine with a touch display, a mobile device, a push button, or a computer with a keypad. From an industrial view point, the most valuable aspect of HMI technology is the ability to closely monitor production and respond to changing production demands, which improves efficiency and decreases downtime. These benefits are a result of improved diagnostics and monitoring.
A perfect designed HMI solution not only increasing productivity for the operator but also provides a line of sight into the system to control or maintain the machine. Alarming is the best example of an HMI function that provides visual indicators of a machine’s issue and its extremity. Traditional HMI solutions were stand-alone, isolated terminals that were deployed by any manufacturer as part of a machine. New HMI solutions are either pre-configured to send data to the cloud. The IoT is changing manufacturing plants. More customers are expecting industrial HMIs to work like their mobile phones in the way they interact with them. This is driving a big change in the ability to see an industrial HMI and how it is expected to operate.
MI is implemented in an industry where human intervention with a machine or automated device is necessary. This could be in a plant, building, machine or even a vehicle. The level of integration and experience may vary, but HMI can be added to just about any application type.HMI is mainly used in manufacturing—from the automotive industry to the highly regulated food and pharmaceutical industries. Process industries heavily use HMIs, such as in oil and gas, and mining operations in which many processes are managed remotely from the control room.
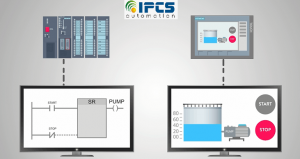 In the rise of Industry 4.0 and the IIOT has made it even easier, as we can turn our smartphones into a form of mobile HMI, and technology such as smart watches has made HMI wearable, increasing accessibility and ease of use.
In the rise of Industry 4.0 and the IIOT has made it even easier, as we can turn our smartphones into a form of mobile HMI, and technology such as smart watches has made HMI wearable, increasing accessibility and ease of use.
