Molded case circuit breakers are a type of electrical protection device that is commonly used when load currents exceed the capabilities of mcb. They are also used in applications of any current rating that require adjustable trip settings, which are not available in plug-in mcb.
All these adjustable trip settings actually shape the time-current curve of a circuit breaker and allow proper tripping according to the network parameters
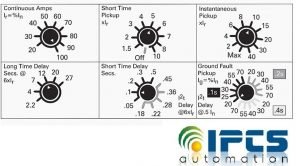
- Continuous Amps
- Long-Time Delay
- Short-Time Pickup
- Short-Time Delay
- Instantaneous Pickup
- Ground Fault Pickup
- Continuous Amps (Ir) (Thermal setting)
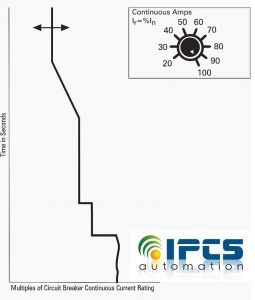
Continuous Amps sets the level of current the circuit breaker will carry without tripping. Ir is a percentage of the circuit breakers nominal rating (In). Continuous amps can be adjusted from 20 to 100 percent of the circuit breakers nominal rating. In normal Load a bimetallic element is heated by the normal load current, the bimetallic element does not bend. If the temperature or current increases over a sustained period of time, the bimetallic element will bend, push the trip bar and release the latch. The circuit breaker will trip. If MCB is 1000A Rating but Full Load current is 600A than MCCB Rating can be changed from 1000A to 600A by setting it 0.6, Now Ir=0.6XIn = 0.6×1000 = 600Amp
Standard Practice:
Trip in less than two hours for a current equal to for 120% of Ir for an electronic trip unit and for 130% of Ir for a thermal-magnetic trip unit
For a higher fault current, the trip time is inversely proportional to the fault current value
- Long-Time Delay
Long-time delay is used in conjunction with Continues amps setting which causes the breaker to wait a certain amount of time to allow temporary inrush currents, for example when a motor is starting, the CB should pass without tripping.
The adjustment is from 2.2 to 27 seconds at six times the continuous amps (Ir) setting.
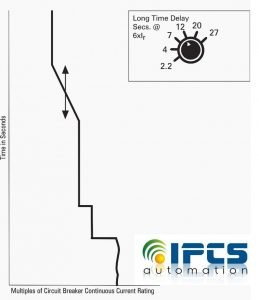
As shown below, the long-time delay effects the position of an I2T slope. This means that lower levels of current will allow the breaker to remain online for longer periods of time. The long-time delay sets the time period that the circuit breaker can carry an over current (below the short-time or instantaneous pickup current level) before tripping.
- Short-Time Pickup (magnetic setting)
Short time pickup is used for short circuit protections. The short-time pickup function determines the amount of current the circuit breaker will carry (less than instantaneous trip value) for a short period of time. If the current suddenly or rapidly increases, the magnetic element will attract the trip bar, release the latch, and the circuit breaker will trip.
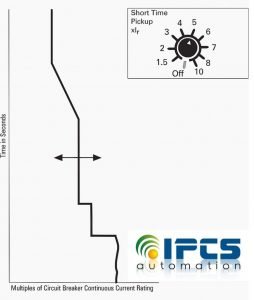
Short-time pickup is adjustable from 1.5 to 10 times the trip unit ampere setting (Ir).
For example, a 1000 ampere frame can be adjusted to trip anywhere from 1500 to 10,000 amps.
- Short-Time Delay
Short-time delay, used in conjunction with short-time pickup, controls the time involved in postponing a short-time pickup trip.
There are two modes: fixed time, or I2T ramp. Fixed time is adjustable from .05 to .5 seconds. The I2T ramp mode is adjustable from .18 seconds to .45 seconds, providing a short inverse time ramp.
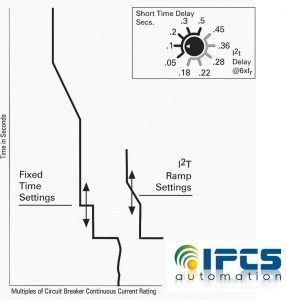
This allows better coordination with downstream thermal-magnetic circuit breakers and fuses. A fixed instantaneous trip point of 10,000 amps trips the breaker automatically and overrides any pre-programmed instructions.
- Instantaneous Pickup
Instantaneous pickup is used to trip the circuit breaker with no time delay at any current between 2 and 40 times the breaker’s continuous ampere setting (Ir).
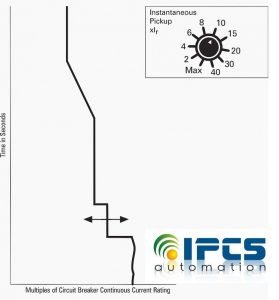
For example instantaneous pickup has been set to 10 times the continuous amp 10 x 1000 = 10,000 amps (If continuous amp setting of 1000 amps.)If the continuous amp setting had been 300 amps, setting the instantaneous pickup at 10 would make the instantaneous setting equal to 3000 amps.
The instantaneous function will override the short-time function if the instantaneous Pickup is adjusted at the same or lower setting than the Short Time Pickup.
6. Ground Fault Pickup
Ground fault pickup controls the amount of ground fault current that will cause the breaker to trip. The adjustment can be set from 20 to 70% of the maximum breaker rating.
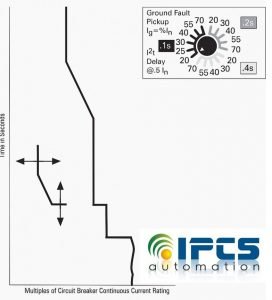
The ground fault pickup is divided into three sections; .1s, .2s, and .4s. This feature adds a time delay of .1, .2, or .4 seconds to the breaker’s trip when a ground fault occurs.
