Proximity sensor is a device that detects objects within its vicinity without any physical contact up to nominal range. A proximity sensor often emits or radiates a signal in the form of electromagnetic radiation and looks for changes in it or return signal. These changes (or return signal) in electromagnetic radiation are convert into an electrical signal. The object being sensed is referred to as the target of the proximity sensor.
Proximity sensors have a high reliability and long life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact between the sensor and its target. Proximity sensors commonly used in many industrial applications. They also used in vehicles for detecting the proximity of other vehicles as well as for parking-assist functions.
Sensing distance of proximity sensor – Terminology
Nominal sensing distance (Sn).
The rated operating distance for which the proximity sensor is designed. It does not depend on any variations in temperature, voltage, manufacturing tolerances, etc.
Real sensing distance (Sr).
It is measured at the rated voltage (Un) and at rated ambient temperature (Tn). It must be 90% -110% of the nominal sensing distance (Sn)
0.9 Sn ≤ Sr ≤ 1.1 Sn.
Usable sensing distance (Su).
The usable sensing distance is measured at the limits of the permissible variations of the supply voltage (Ub) and the ambient temperature (Ta). It must be 90% – 110% of the real sensing distance (Sr)
0.9 Sr ≤ Su ≤ 1.1 Sr.
Assured operating distance (Sa).
Assured operating distance is the operating zone of the proximity sensor.it is between 0 and 81% of the nominal sensing distance (Sn)
0 ≤ Sa ≤ 0.9 x 0.9 x Sn.
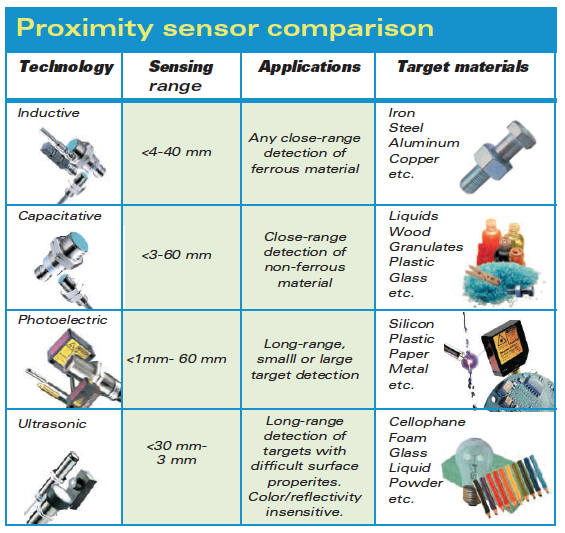
Comparison of proximity sensors based on sensing range
The sensing range must selected by considering the effects of factors such as the temperature, the sensing bodies (targets), surrounding objects, and the mounting distance between Sensors. A Separate Amplifier model used, when high precision detection is required.
Inductive proximity sensors
Inductive proximity sensors used for non-contact sensing of metallic targets. These have a relatively narrow sensing range due to the limitations of magnetic field. The sensing range commonly varying from fractions of millimeters to 60 mm. Even though longer- sensing range sensor are also available.
An inductive proximity sensor has a sensing range that determines the functional distance between a target and the sensor’s surface, and it refers to the shape of the electromagnetic field emitted from the sensor.
Some of the factors that can influence the sensing range are
The ferrite core’s size
Size of sensing object (target)
Environmental electrical and mechanical conditions
Surrounding temperatures
Shape of sensing object
Capacitive proximity sensors
Capacitive proximity sensors are non-contact type devices that can sense the presence or absence of any object. Capacitive type sensing are slower than inductive sensing because of the charging plates. These sensors usually have a longer sensing range than the inductive sensors, and it typically in between 3 and 60 millimeters. The detection range depends on plate diameter of sensor, as it measure dielectric gaps. Many capacitive sensors are equipped with sensitivity adjustment controls for the detection range, allowing them to compensate for sensing object and application conditions.
Ultrasonic proximity sensors
Ultrasonic proximity sensors used in many automated production processes. They measures the distance to a sensing object using ultrasonic sound waves. This makes them most suitable for a variety of applications, including the distance measurement, long-range detection of clear glass and plastic, continuous fluid and granulate level control, and paper, sheet metal, and wood stacking. It is used for long range detection of sensing object with difficult surface properties The sensing range of ultrasonic proximity sensors are extend to 2.5m
Photoelectric sensor
A photoelectric sensor used to determine the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter and a photoelectric receiver. They mainly used in manufacturing industry. There are three different types: opposed (through beam), retro-reflective, and proximity sensing (diffused). The maximum sensing range of through beam type is 50 m (164.042 ft) and that of diffused type is 5m (16.404 ft). These long sensing range of photoelectric sensor make them suitable for a variety of applications.
