A relay is a type of electromechanical switch used in power supplies, counting systems and many other applications. It is used to control a large current with a small current. Most relays require a small continuous voltage to stay on. A latching relay is different. Latching relays opens or close its contacts by the power input. Even after this input power is interrupted, this relay maintains its state until it receives the next inverting input. This type of relay also called keep relay or stay relays or impulse relays. Latching relays is used in situations where energy efficiency is important, but also in situations where you need the relay to maintain its state – typically so that the user can press a push button to close the relay contact, and press a second push button to open the relay contact again. The relay remembers which button was pressed last.
Working
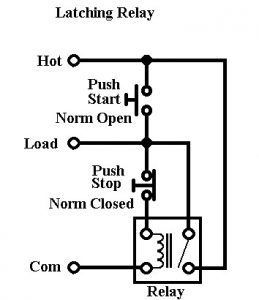
The above circuit has two push buttons – one is normally open (NO) push button, and the other is normally closed (NC) push button. When the NO push button is pressed, input supply goes across the coil, and then energizes the relay. This closes the internal relay contact. Then power source feeds through this contact to arrive at the relay coil keeping it energized even when the NO push button is released. Thus, considerable energy is saved by these relays. In order to de-energize the relay, the normally closed (NC) push button needs to be pressed which cuts the connection feeding through contact and energizing the coil. With that button pressed, there is no voltage across the relay coil and so it de-energizes.
Applications
There are numerous uses in the present electric gadgets for latching relays. These include industrial or commercial machines, for example, vehicle wash equipment that uses dryers and pumps. HVAC and refrigeration, industrial cleaning equipment, anti condensation equipment are examples of equipment that uses latching relays. Commercial coffee machines and commercial cooking equipment also use latching relays. In computer memories, latching relays were replaced by delay line memory, which thus was supplanted by a series of ever-faster and ever-smaller memory technologies. An earth leakage electrical switch incorporates a particular latching relay. Early computers frequently put away bits in a magnetically latching relay, for example, ferreed or the later remreed during the 1ESS switch.
