Topics:
- History of Fire Sprinklers
- Types of Sprinkler Systems
- Types of Sprinkler Heads
- Future of Fire Sprinklers
- Facts about Sprinkler Systems
History of Fire Sprinklers:
History of Fire Sprinklers Officially developed and used by Henry Parmalee in 1874 to protect his piano factory Used clay and wood pipes with holes drilled into them A tank on the roof of the structure was drained during a fire and released the water into the pipes Winter was a problem, and making sure someone was watching at all times
Timeline:
Fire Sprinkler System Time Line: 1806 – John Carey designs a system of perforated pipes, plungers, and burning strings. 1812 – Colonel William Congreve designs perforated pipes with valves. 1875 – Parmelee invents the first modern sprinkler. It consists of shell and soldered brass cap. 1882 – Grinnell invents an improved sprinkler that can withstand higher pressures and distributes water more evenly. 1896 – N.F.P.A. is officially formed and publishes codes for automatic sprinkler installation.
Types of Sprinkler Systems:
- Wet Sprinkler System
- Dry Sprinkler System
- Deluge Sprinkler System
- Pre-Action Sprinkler System
Parts of a Sprinkler System:
- OS&Y- Outside Stem and Yoke
- PIV- Post Indicator Valve
- Main Control Valve- Controls water for whole system
- Main Drain- Drains System
- Inspector Test- Tests system
- Alarms- Water flow or Air Alarms
Components of a Sprinkler System:
- Underground brings water from the City Mains to your building
- Water is then sent through a backflow
- All Systems usually require an FDC or Fire Department Connection to increase the water pressure during a fire
- Enters either the fire pump where it is pumped to a certain pressure, or is released into the Riser
- Risers “rise” vertically through the floors to feed the Branch Lines
- Branch Lines then extend off the Risers and Mains horizontally to bring water to all the sprinkler heads
Wet Systems:
- Water is in branch lines and at the sprinkler heads at all times
- Wet Systems cannot be in areas that may freeze
- Water pressure must be maintained at all times
- Water Pumps are put in place to keep water pressure at a certain PSI
- There is no delay in time that water is put on the fire
- Require the least amount of maintenance
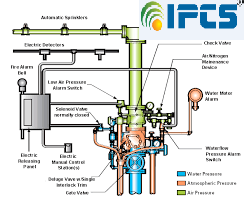
Dry Sprinkler System:
- Require Air Pressure instead of water in the Branch Lines
- The Air Pressure holds down a Clapper Valve, so that water cannot be introduced into the system, unless the air pressure is lost
- Used in areas that may freeze
- An air compressor keeps a constant pressure in the system
- When a Fire releases a sprinkler head, the air is released from the piping, and stops holding down the valve that was holding the water back, and water is released
- Standpipes are used in stairwells to have a water way established for hand lines
- These systems have a high maintenance cost, due to c
 orrosion in the pipe with only air, and a little bit of water
orrosion in the pipe with only air, and a little bit of water - Might take up to 60 seconds to get water on the fire, depending on how big the system is
Deluge:
- Deluge Valves are used in special areas
- Sprinkler heads are open at all times
- Used in High Hazard areas
- Deluge Valve opens during a smoke or heat detection
- Deluge systems are needed where high velocity suppression is necessary to prevent fire spread
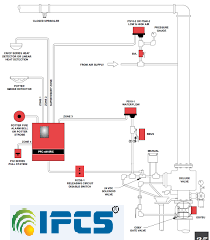
Pre-Action Systems:
- Same as a Dry System
- Water is held back by an electronically operated valve
- Two things need to happen before water is released
- The detection system must identify that there is a problem with smoke or flame
- Water is then released into the piping
- Secondly the sprinkler heads must be activated and released to put water on the fire.
Types of Sprinkler Heads
- Pendants
- Uprights
- Sidewalls
- Special Coverage
Fire Sprinkler Colours
- 135-170 degrees = Red
- 175-225 degrees = Green
- 250-300 degrees = Blue
- 325-375 degrees = Purple
- 400-650 degrees = BLACK
Upright Head:
- Sits on top of the piping
- Sprays water up towards the deflector
- Cannot be used as a pendant
Sidewall Head:
- Comes out of a wall to protect hallways or small rooms
- Has a fan shaped deflector
- Used in Hallways or special areas that are not big enough for regular heads

Types of Sprinkler Systems:
- Residential- Just beginning to become popular
- Piping is made of a special CPVC plastic
- Industrial- Heavy amounts of fire load require many heads.
- Piping is usually made of metal

Future of Fire Sprinklers:
- Home fire sprinklers are just beginning to be made more accessible
- Insurance rate cuts
- Better protection
- Aqua-Flex Heads are easier to install, and cuts back on labor costs More special area heads are being created and tested


 orrosion in the pipe with only air, and a little bit of water
orrosion in the pipe with only air, and a little bit of water