Motor:
An electric motor is an electric machine that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. Electric mo tor may be classified by electric power source type, internal construction, application, type of motion output, and so on.A magnetic field is created around an electrical conductor when an electric current is passed it. This is known as electromagnetism. The magnetic field around electrical conductor can be strengthened by winding them into a coil around an iron core.
tor may be classified by electric power source type, internal construction, application, type of motion output, and so on.A magnetic field is created around an electrical conductor when an electric current is passed it. This is known as electromagnetism. The magnetic field around electrical conductor can be strengthened by winding them into a coil around an iron core.
Controlled motion:
In many motors, the rotor spins continuously, with no way of precisely controlling the motor’s rotational position and speed. Stepper motors and servo motors are two widely used kinds of motors whose position and speed can be precisely controlled. Generally it requires a relatively sophisticated controller with high speed pulse train outputs. It is used in applications such as robotics, CNC machinery or automated manufacturing.
A stepper motor is a digitally controlled motor that allows precise control over the position of the motor’s rotor. Changes in the digital input rotate the motor’s rotor by a precise amount, which is called a step or step angle. Depending on the motor ,this step angle may be as small as 1 degree (or less) or as large as 45 degree. The motors position can then be commanded to move and hold at one of these step without any feedback sensor. The stepper motor can convert a train of input pulses (typically square wave pulse) into a precisely defined increment in the shaft position. Each pulse moves the shaft though a fixed angle.
Working of stepper motor:
One electromagnet is given power, which magnetically attracts the gear’s teeth. When the ge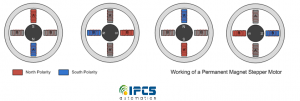 ar’s teeth are aligned to the first electromagnet, they are slightly offset from the next electromagnet. So when the next electromagnet is turned on and the first is turned off, the gear rotates slightly to align with the next one, and from there the process is repeated. Each of those rotations is called a “step” ,with an integer number of steps making a full rotation. In that way, the motor can be turned by a precise angle.
ar’s teeth are aligned to the first electromagnet, they are slightly offset from the next electromagnet. So when the next electromagnet is turned on and the first is turned off, the gear rotates slightly to align with the next one, and from there the process is repeated. Each of those rotations is called a “step” ,with an integer number of steps making a full rotation. In that way, the motor can be turned by a precise angle.
Types-Permanent Magnet:
The stater and rotor poles of a permanent magnet stepper are not teethed. Instead the rotor have alternative north and south poles parallel to the axis of the rotor shaft. The resolution of the permanent magnet stepper can be increased by increasing number of poles in the rotor or increasing the number of phases.
Types-Variable reluctance:
The variable reluctance stepper has a toothed non magnetic soft iron rotor. When the stater coil is energized the rotor moves to have a minimum gap between the stater and its teeth.
Types-Hybrid stepper:
A hybrid stepper is a combination of both permanent magnet and the variable reluctance. The magnetic rotor has two cups .One for north poles and second for south poles. The rotor cups are designed so that the north and south poles arrange in alternative manner.
