A Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU) is a digital based electronic device. A device can collect data’s from the real world and transmit that data’s without loss to the specific object (Controller, software etc.,). We called that device name as Remote Terminal Unit or Remote Telemetry Unit. RTU (Remote Telemetry Unit) uses either wired or wireless communication methodologies to transfer data from remote location to control room.

Photo Courtesy: Siemens
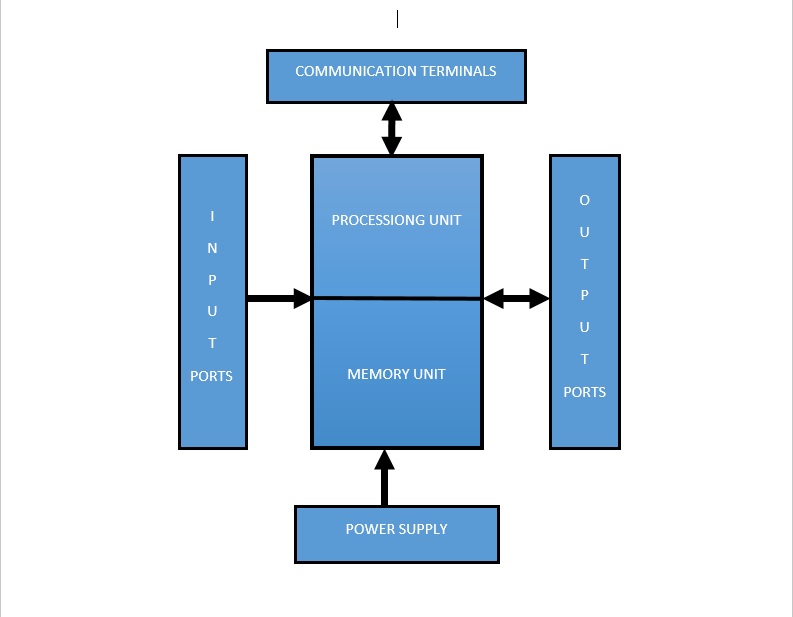
RTU circuitry including the following parts,
- Power supply
- Input ports
- Output ports
- Communication terminals
Architecture of RTU
Power Supply:
RTU requires 24vdc power supply for uninterrupted running. Mostly RTU’s are placed in remote areas, that areas don’t have direct power supply contact. So most of the places RTU has powered by batteries. Generators or other renewable energy sources help to power up batteries. Solar panels are mostly preferred for remote location power generation.
Input Ports:
The input ports of the RTU varies in functionality by a little from conventional PLC inputs. These inputs serve as an interface between the hardware and software elements of the RTU system for acquiring real time data. The RTU has collect real world input data’s from different digital and analog based devices (Sensors, Transmitters). Digital data’s can directly process in RTU but Analog data’s requires ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) module because RTUs processing area only digital form of data. The RTUs input area accepts Digital, Analog & frequency counter etc., category devices.
Output Ports:
The Output ports of the RTU varies in functionality by a little from conventional PLC outputs. These outputs serve as an interface between the hardware and software elements of the RTU system for delivering data’s to the field. Output devices has got the data’s from the RTU in Digital and analog form. Analog area needs additional module named DAC for Digital to Analog Conversion, Because RTU relays only Digital data. Relay and Contactor based wiring methods helps to activate real world output devices like Motors, Pumps, Valves etc.,
Photo Courtesy: Siemens
Communication Terminals:
Communication is the main part that differs RTU from PLC. Prime aim of the RTU is to transfer data from remote location to control room. RTU supports both wireless and wide area network applications and works well on High and low speed networks. A RTU may be interfaced to multiple master stations and IEDs (Intelligent Electronic Device) with different communication media (usually serial (RS232, RS485, RS422) or Ethernet). An RTU may support standard protocols (Modbus, IEC 60870-5-101/103/104, DNP3, IEC 60870-6-ICCP, IEC 61850 etc.) to interface any third party software. Most of the RTUs have supports GSM & GPRS based data transfer methods.
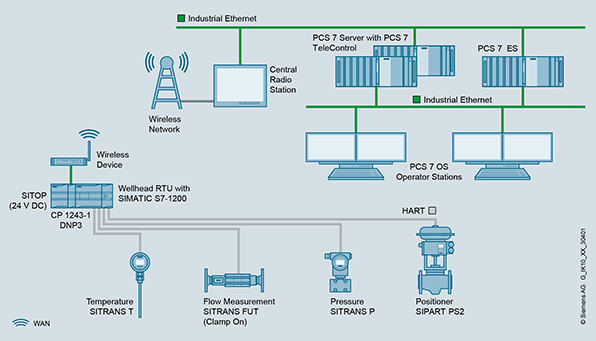
Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU) has mainly helps in DCS & SCADA based systems for acquiring data from the field. The above image explains RTU collects data from different devices like Flow transmitter, Pressure Transmitter etc., and is not processed in RTU. RTU just collects and handles data, then send the collected data to the main operator station. The Main Operator station will have dedicated control system to decide what has to happen next. So RTU is just a Data Acquisition Device.