Camera Image Sensors

The easiest way to understand the image sensor is to think of itas the equivalent of a piece of film. The image is exposed onto the sensor in the same way that it would be exposed onto a piece of film in a 35mm film camera.
Digital camera sensors consist of a number of pixels which collect photons (energy packets of light) that are converted into an electrical charge by the photo diode. In turn, this is converted into a digital value by the analog to digital converter (ADC). This allows the camera to process these values into the final image.
All digital cameras have an image sensor that is used to capture information and create a photograph. There are two primary types of image sensors – CMOS and CCD – and each has their own advantages.
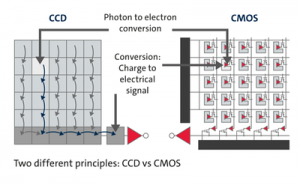
CCD Image Sensor:
CCD (Charge Coupled Device) sensors convert pixel measurements sequentially using circuitry surrounding the sensor. CCDs use a single amplifier for all of the pixels. CCDs are manufactured in foundries with specialized equipment and this is reflected in their often higher cost.
There are some distinct advantages to a CCD sensor:
- Less noise and generally higher quality images, particularly in low light conditions.
- Known for having a better depth of color because the dynamic range of the sensor is often twice that of CMOS sensors.
- Traditionally, CCD sensors have a higher resolution and are more sensitive to light.
CMOS Image Sensor:
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) sensors convert pixel measurements simultaneously, using circuitry on the sensor itself. CMOS sensors use separate amplifiers for each pixel. CMOS sensors are more commonly used in DSLRs as they are faster and cheaper. Both Nikon and Canon use CMOS sensors in their high-end DSLR cameras.
The CMOS sensor also has its advantages:
- Known to be faster at processing images because the active pixels and ADC are on the same chip.
- Lower power consumption, as much as 100 times less than a CCD.
- CMOS sensors can integrate camera functions like auto exposure, color encoding, and image compression directly in the chip.
- When an image is overexposed, it can lead to ‘smearing’ around the pixels affected with CCD sensors. CMOS technology prevents this effect.
- The manufacturing process is easier, much like any microprocessor, and this makes them less expensive.
- As technology has advanced and CMOS sensors have become a new standard, the quality of them has improved greatly since their introduction.
